How To Optimize your First Design
In this section, you’ll go through the essential steps to optimize your first design with FilmOptima.
Prerequisites:
FilmOptima offers three different merit functions: 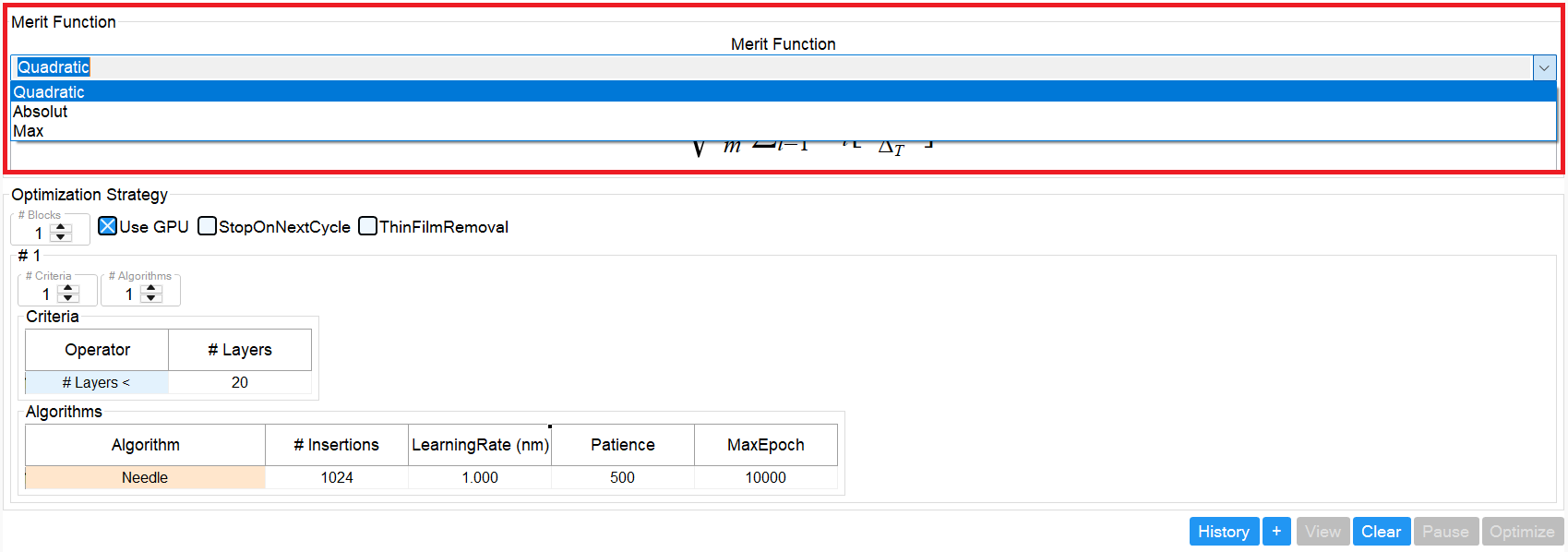
In most cases Quadratic is a good starting point.
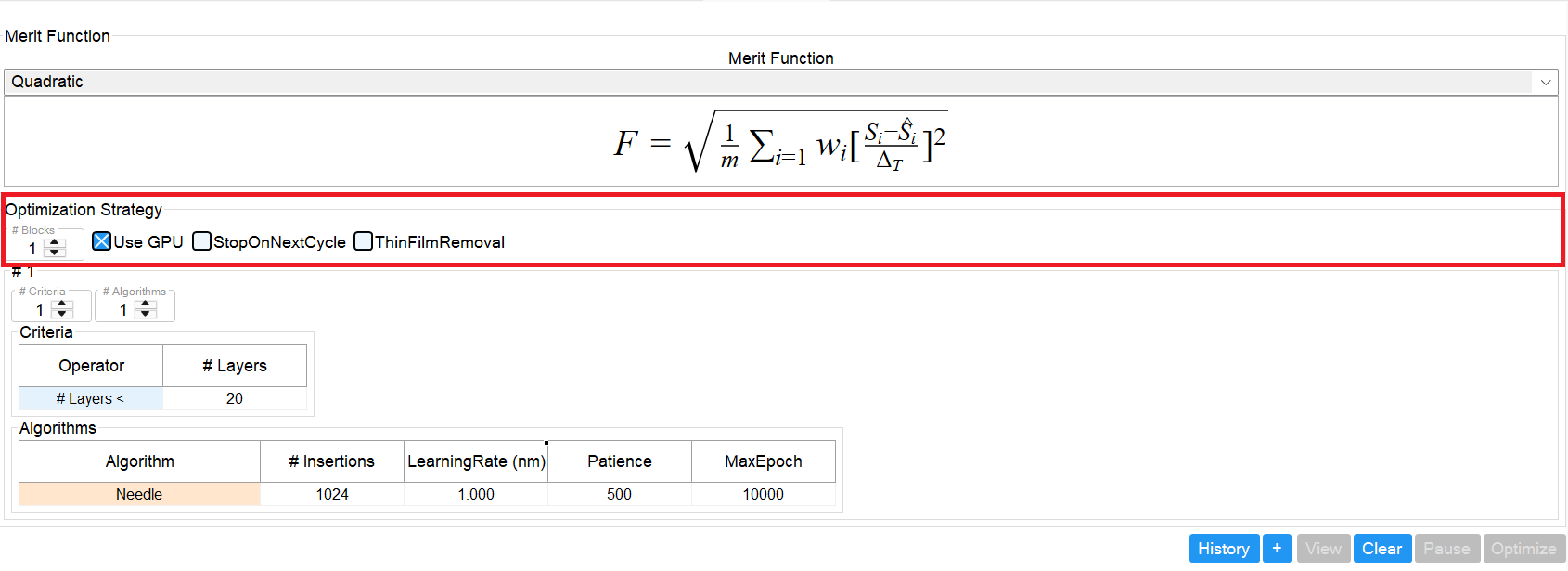
#Blocks – Defines the number of optimization blocks to run consecutively, provided the current design meets the defined conditions. (See Step 3 for more details.)
UseGPU – Enables GPU acceleration for the optimization. Strongly recommended for performance.
StopOnNextCycle – When checked, the optimizer performs a single optimization cycle and then stops.
ThinFilmRemoval – When checked, layers thinner than the specified threshold are removed after each optimization cycle.
⚠️ Caution: This may cause optimization to stall. For example, if Needle algorithm inserts a very thin layer and it is immediately removed, progress will be blocked.
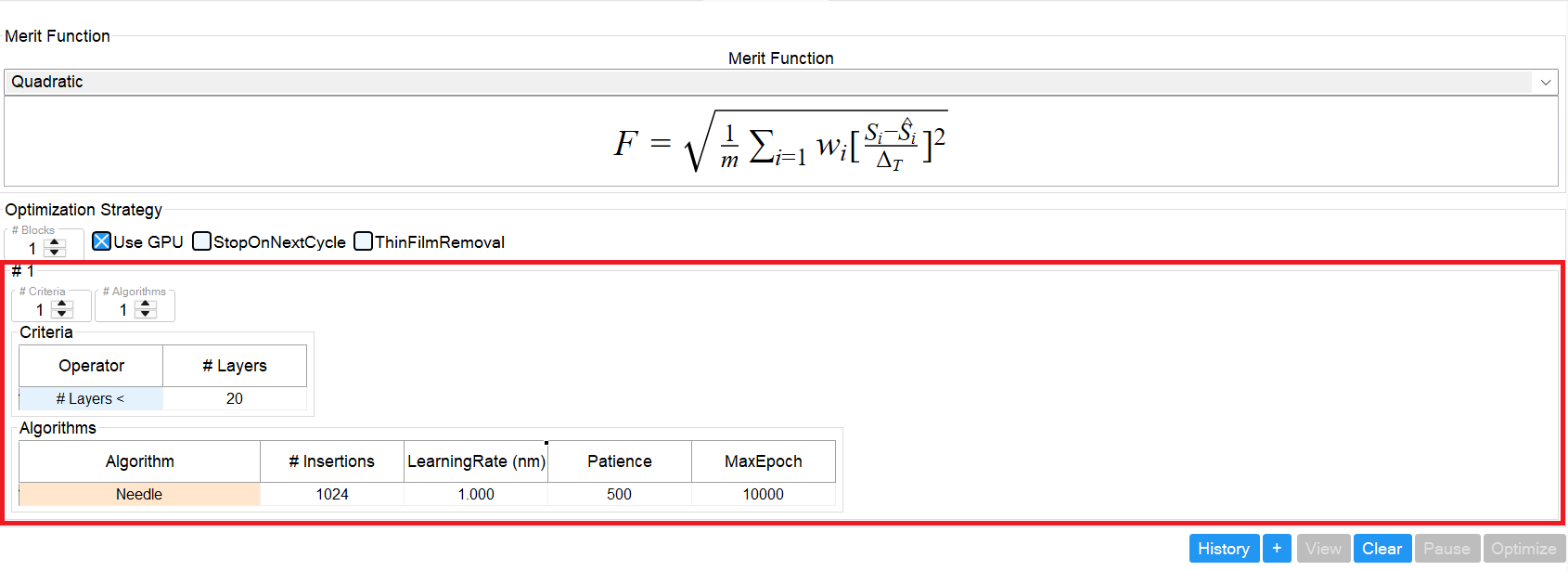
Block Parameters
#Criteria – Specifies the number of criteria for the current optimization block. Conceptually, this works like an if-statement with logical ANDs between criteria. If all conditions evaluate to true, the optimizer executes the algorithms defined in this block.
#Algorithms – Specifies the number of algorithms contained in this block.
Criteria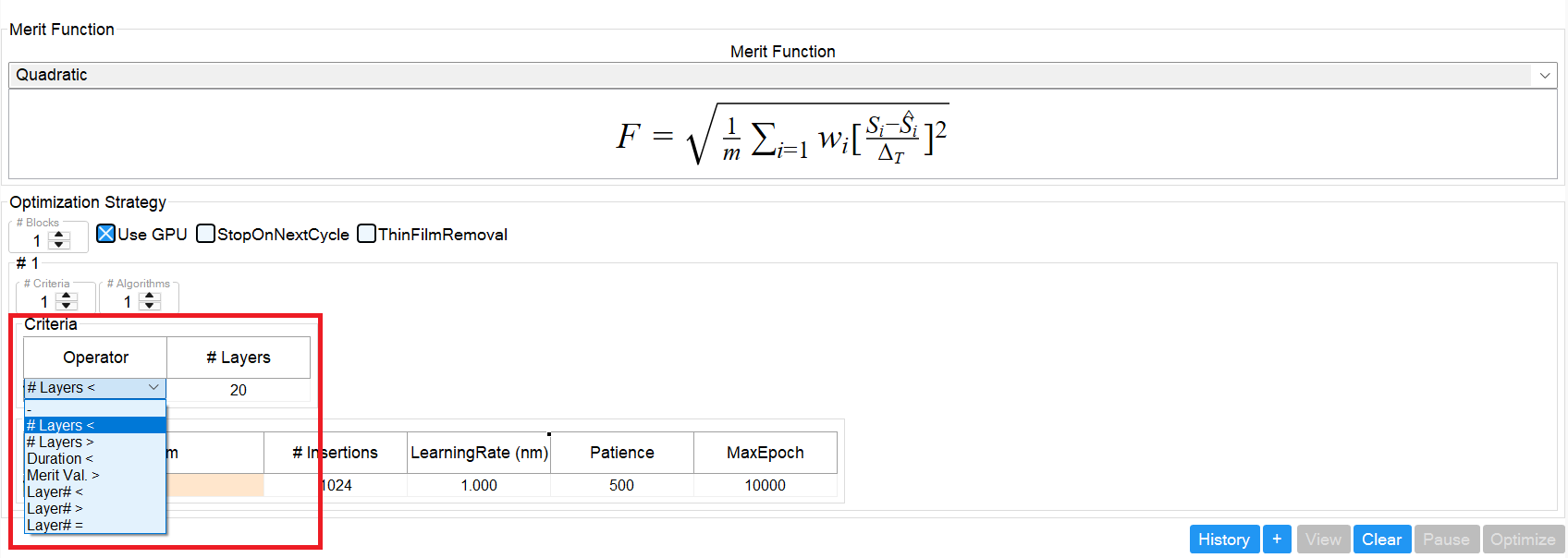
Algorithms
FilmOptima supports three categories of algorithms: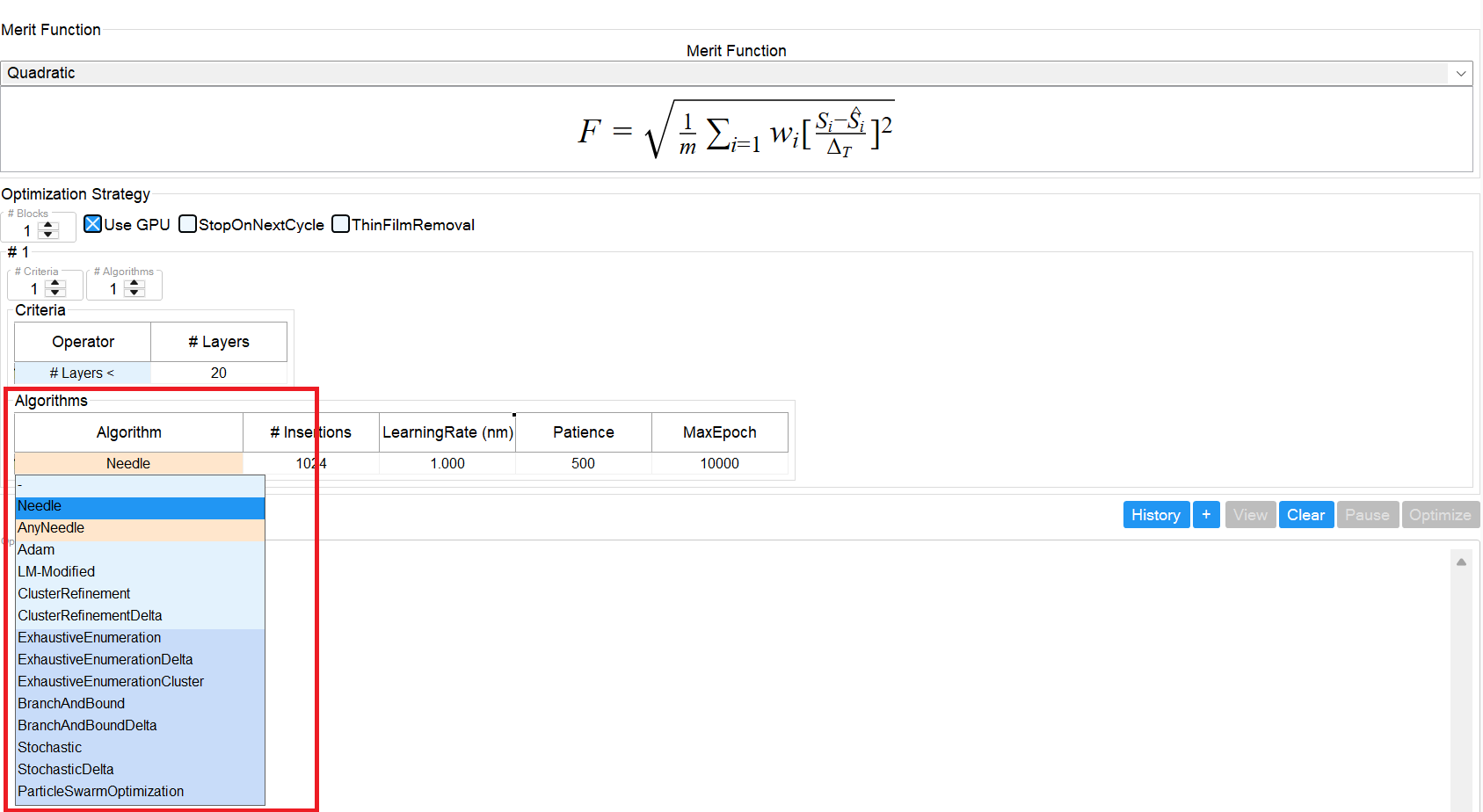
Synthesis (light orange) – Adds one or more layers to the stack, followed by a local optimization of all layer thicknesses.
Refinement (bright blue) – Performs a local optimization without changing the number of layers.
Global Optimization (light blue) – Performs a global optimization without changing the number of layers.
Nested Algorithms
Synthesis and Global Optimization are often nested optimizers, as each iteration is followed by a Refinement algorithm that further adjusts layer thicknesses. FilmOptima employs Adam as the nested refinement method.
Accordingly, the final three parameters in these algorithms—Learning Rate, Patience, and Max Epoch—refer specifically to the Adam optimizer.
Learn more about the algorithms in the algorithms section.



